Gender identity is a very important issue in most societies. In many instances the question of whether the newborn is a boy or girl actually precedes the question “is he/she healthy?” Thus, not being able to categorize an individual at birth as a male or female could be devastating for any parent, as well as for the affected individual. Recommendations for sex rearing continues to be challenging, requiring the involvement of medical, surgical, and psychological professionals working together in multispeciality clinics. Patients need to be monitored for years to ensure that their subsequent adaptation to the assigned gender progresses as expected. Despite several genes being associated with sex reversal and genital ambiguity, most of which affect males, there are still cases for which the genetic candidate remains unknown. The issue becomes more complex when we consider females, since very little is known about how ovaries develop. So limited is our understanding of ovarian formation that a bias that ovaries develop only when testis genes are not expressed has been ingrained. However, since studies of humans with intersex abnormalities have suggested that ovarian formation is an active process, it is now reasonable, even compelling, to screen for ovary-determining genes. This chapter will discuss early mammalian sex differentiation in mouse and man and also subsequent development of female reproductive organs, when possible, relating mouse knockout phenotype to human disease.
1. Formation, proliferation, and migration of mouse primordial germ cells
Primordial germ cells (PGC), the progenitors of the oocytes and spermatocytes, become committed to the germ cell lineage around E6.0 when a group cells at the proximal region of the epiblast are induced to express Prdm1 (Blimp1), which represses Hox and other somatic genes, upon exposure to BMP2, BMP4 and BMP8b signals emanating from the extra-embryonic ectoderm (Lawson (1999); Ohinata (2005); Saitou et al., (2005); Ying et al., (2000)). BMP4 signals through ACVR1 (ALK2), a type I BMP receptor, which is expressed in the visceral endoderm at the junction of the extra-embryonic ectoderm and epiblast (de Sousa Lopes (2004)). PGC then migrate posteriorly in the embryo to the base of the allantois by E7.25 as a result of gastrulation, at which time they are more easily identified by their expression of alkaline phosphatase and Dppa3 (Stella). These studies indicate that both the extra-embryonic ectoderm and visceral endoderm are necessary for the initial recruitment of proximal epiblast cells that lay scattered near the junction with the extra-embryonic ectoderm to become precursors of PGC (see Figure 1; MacLaughlin and Donahoe (2004)).
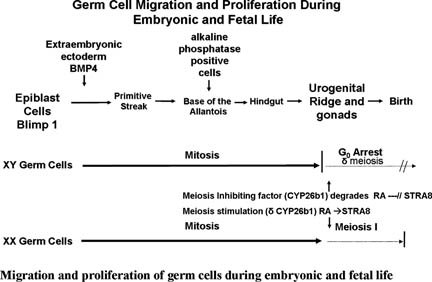
Figure 1.
After arriving at the base of the allantois, PGC start their migration toward the genital ridges via the hindgut and dorsal mesentery (Donovan et al., (1986)). The initial migration appears to be passive as PGC are caught up and moved away by the forming hindgut. This is then followed by an active migratory process, which involves cell adhesion molecules, survival factors, and chemotactic signals (Anderson (1999); Molyneaux (2003)). Throughout their entire migratory phase, PGC undergo mitotic divisions and are observed as string of cells joined by cytoplasmic bridges. PGC lose their migratory phenotype soon after their entrance into the genital ridges and become dissociated into individual cells that will continue to divide forming isolated groups of germ cells, or cysts (Pepling and Spradling (2001)). Correct PGC migration and colonization of the gonads are important developmental processes than when faulty can lead to abnormal gonadal development and to the formation of childhood germ cell tumors, which account for 2.9% of all malignant tumors in children below the age of 15, 50% of which are extragonadal (Cools et al., (2006); Gobel (2000); Schneider (2001)).
2. Genital ridge formation
At about E10.0 in the mouse, a thickening in the ventro-medial aspect of the intermediate mesoderm gives rise to the urogenital ridges, the anlagen of the gonads, Müllerian and Wolffian ducts et al., (Swain et al., 1999)). The gonads are a combination of PGC, which migrate from the base of the allantois to contribute to the germ cell lineage, and somatic cells migrating from the mesonephros and coelomic epithelium (Donovan et al., (1986); Buehr et al., (1993); Capel et al., (1999)). Mutation studies have implicated several genes in early gonadal formation. Mice deficient for steroidogenic factor-1 (Sf1) do not develop gonads or adrenal glands and die within 8 days after birth from renal insufficiencies (Luo et al., (1994)). Mutations in Wilm's tumor 1 (Wt1) are found in patients with Denys-Drash syndrome, Frasier syndrome, and Wilm's tumor, associated with aniridia, GU malformations, and mental retardation (WAGR) patients, all of which are characterized by genitourinary abnormalities as well as a predisposition for Wilm's tumor (Reddy and Licht (1996)). Wt1 homozygous mutant mice show abnormalities of the urogenital system et al., (Kreidberg et al., 1993)). Mice carrying mutations in the homeobox genes Lhx1 (a.k.a. Lim1), Lhx9 and Emx2 also show aberrant genital ridge formation (Miyamoto et al., (1997); Shawlot and Behringer (1995)). The common theme among these mutations is that genital ridges begin to form, but start to degenerate soon thereafter.
3. Testis development
Once the genital ridges are formed, the next decision is whether to differentiate into testes or ovaries. The list of genes known to have a role in testis development is extensive, with most of these genes affecting testis cord formation and somatic cell migration. In brief, the determination of the male sexual phenotype in mammals begins with expression of the testis determining factor Sry on the Y-chromosome (Koopman et al., (1991); Sinclair (1990)). Normally, in the presence of Sry the bipotential fetal gonads develop into testes (Koopman et al., (1991)). Sox9 is another Sry-related HMG box gene known to be required for testis development. Humans with heterozygous null mutations for SOX9 develop campomelic dysplasia, a lethal bone malformation syndrome (Foster (1994)). Interestingly, approximately 75% of XY SOX9 heterozygotes also show sex reversal (Mansour et al., (1995)). Mutations in the mouse polycomb homologue Cbx2 (M33) results in different degrees of XY sex reversal as well as homeotic transformations (Bel (1998); Katoh-Fukui (1998)). Pdgfrα is need for mesonephric cell migration into the testis and leydig cell differentiation, while Fgf9 is required for the proliferation of the Sertoli cell lineage (Colvin et al., (2001)). GATA4 and FOG2 form heterodimers, which are needed for normal testis cord formation (Tevosian (2002)). The complexity of testis formation is further exemplified by the observation of male sex reversal in animals carrying compound homozygous mutations in all of the insulin receptors, Insr, Igf1r and Insrr (Nef (2003)). Mice with individual mutations in any of these insulin receptor genes show normal testis development. In addition, mice with a null mutation in Dax1, a gene initially thought to play a role in ovarian development, only show abnormalities in testis cord formation and spermatogenesis (Yu et al., (1998)).
At the cellular level, testis formation has also been well documented. Coelomic epithelial cells labeled with the lipid-soluble fluorescent dye, DiI, were seen entering the testis between E11.2 and E11.4 to contribute to the Sertoli cell population and interstitial compartment. However, cells entering the testis between E11.5 and E11.7 did not contribute to the Sertoli cell population, indicating that there is a finite time for the contribution of coelomic cells to the Sertoli cell lineage (Karl and Capel (1998)). In a series of experiments where an XX gonad was “sandwiched” between an XY gonad and an XX mesonephros, it was observed that mesonephric cells migrated into the XX gonad to form cord structures composed of XX Sertoli cells (Tilmann and Capel (1999)). The migration was stage specific, requiring the gonads to be no older than E11.5. This migration and differentiation of somatic cells into the different testicular lineages is thought to be mediated by secreted signaling molecules (Capel et al., (1999); Colvin et al., (2001)).
4. Embryonic ovary development
Our understanding of ovarian formation is limited and the idea that ovaries develop only when testis genes are not expressed has been the conventional wisdom. However, studies in humans and mice have challenged the idea of ovarian development being a passive process. For example, duplication of a 160 kilobase (kb) region of Xp21, known as dosage sensitive sex reversal (DSS), has been implicated in XY sex reversal in humans (Bardoni (1994)). Within this region lies the nuclear hormone receptor gene DAX1, as well as a group of genes related to the MAGE family that encodes tumor-associated antigens of unknown function. Evidence that a double dose of DAX1 is responsible for the observed XY sex reversal in humans came from transgenic experiments in mice (Swain et al., (1998)). However, homozygous deletion of the murine Dax1 homolog resulted in normal female gonadal development (Yu et al., (1998)). This severely undermines the possibility of Dax1 being an ovary-determining gene. Based on their sequence similarity and its presence on the X-chromosome, Sox3 has been proposed as a female paralog of Sry (Foster and Graves (1994)), but recent data shows Sox3 to be required for gametogenesis and not differentiation of the gonadal soma (Raverot et al., (2005)).
Wnt4 is the only gene that has been most clearly associated with ovarian development in mice. Homozygous mutant Wnt4 males have normal testicular development, while females show virilization of the ovary with ectopic expression of male steroidogenic genes (Vainio et al., (1999)). In accordance with an active role of Wnt4 in the developing ovary, Yao et al., 2004 provided evidence that the virilization of the Wnt4 mutant ovaries was due to massive germ cell death (Yao (2004)). In the absence of pre-meiotic germ cells, pre-follicle cells form and condense, but they soon degenerate. However, if germ cells are lost after their entry into meiosis, as seems to be the case in the Wnt4 mutant females, follicle cells transdifferentiate into Sertoli cells that aggregate to form seminiferous-like tubules expressing male specific genes (McLaren (1991); Taketo et al., (1993)). Despite Wnt4 involvement in ovary development in mice, the best candidate gene for a role in ovary determination comes from studies in humans (Parma (2006)). Homozygous mutations in R-spondin1 (RSPO1) were found in XX (Sry-negative) males from two independent families. These individuals exhibit complete female to male sex reversal with regression of the Müllerian ducts and normal external virilization, suggesting the presence of testes.
There is also a need to characterize the cellular events leading to the formation of the ovary. It is known that the cellular contributions to the XX gonad differ from those to the XY gonad. As in XY embryos, coelomic epithelial cells colonize the developing ovary, but their proliferation and migration is less extensive, and their differentiation is not cell restricted (Karl and Capel (1998)). When separated from the mesonephros, E11.5 XX gonads developed into smaller, but normal looking ovaries, indicating a less important role for mesonephric cells in ovary morphology, compared to testis development (Martineau et al., (1997)).
5. Postnatal ovary development
Throughout their migration to the genital ridge mitotically dividing PGC are seen as string of cells joined by cytoplasmic bridges (Pepling and Spradling (1998); Greenbaum et al., (2009)). Once in the gonad, PGC, now referred to as oogonia, become clustered into small groups, or cysts, which divide synchronously. By E13.5, oogonia within these clusters enter meiosis, arresting at the (4N) diplotene stage of the first meiosis near the time of birth (see Figure 1). Once in meiosis, germ cells are referred to as oocytes. Cysts breakdown begins at late gestation and early postnatal stages, yielding primordial follicles, which are individual oocytes surrounded by squamous granulosa cells (Pepling and Spradling (2001)). The period between cysts and primordial follicle formation is marked by a surge in programmed germ cell death. Germ cell apoptosis is mediated by the B-cell lymphoma/leukemia-2 (Bcl2) family of apoptotic protein (Knudson et al., (1995); Russell et al., (2002); Stallock et al., (2003)). Mutations in the pro-apoptotic member Bax lead to an increase in germ cell survival, which is reflected by the prolonged fertility of homozygous mutant females (Perez (1999)). In contrast, mutations in the anti-apoptotic member Bcl2, lead to females with a reduced number of oocytes (Ratts et al., (1995)).
The number of primordial follicles present in the neonate determines the pool of oocytes that will be available to the female throughout her reproductive life. However, recent data have suggested that there could be a constant replenishing of new oocytes reaching the ovary through the bloodstream (Eggan et al., (2006); Johnson (2005)). One needs to be cautious in interpreting these results since they are far from conclusive (Begum et al., (2008); Bristol-Gould (2006); Faddy and Gosden (2007)). Follicle development can be divided into preantral (primordial, primary, secondary), tertiary (antral), and luteal stages. The preantral follicle stages are marked by an increased in the layers of granulosa cells surrounding the oocyte, and the formation of the steroidogenic thecal compartment around the follicle. These events are regulated by intraovarian and intrafollicular signals, and not by gonadotropins (Amleh and Dean (2002); Elvin and Matzuk (1998)). Mutations in either Fshß or the gonadotropin releasing hormone (Gnrh) gene do not affect normal preantral follicle development (Cattanach et al., (1977); Kumar et al., (1997); Combelles et al., (2004)), while disruption of genes known to be involved in intraovarian signaling cause preantral follicle arrest. Mutations in the SCF/c-KIT pathway disrupt granulosa-oocyte signaling leading to preantral follicle arrest (Huang (1993)). Similarly, mutations in the oocyte-specific growth differentiation factor 9 (Gdf9) gene also lead to preantral arrest. Mutations in the oocyte specific homeobox gene Nobox, lead to a decreased in cyst breakdown and an absence of follicles developing passed the primordial stage (Rajkovic et al., (2004)). Mutations in the Müllerian inhibiting substance (Mis, a.k.a Amh) gene result in an increase in follicle maturation recruitment, eventually leading to a premature depletion of the ooctye pool (Visser and Themmen (2005)). Mis expression, which is found in granulosa cells of preantral follicles, is shutdown in antral stages. MIS is thought to work as a repressor of FSH, a gonadotropin that induces follicular growth. Communication between the oocyte and granulosa cells is also essential for follicle development. This communication is established at the primordial stage, and is mediated by intercellular membrane channels (gap junctions) (Anderson and Albertini (1976)). Mutations in genes encoding gap junction proteins, such as Gje1 (Cx43) and Gje4 (Cx37), lead to follicular arrest at preantral stages (Juneja et al., (1999); Simon et al., (1997)). Mutations in the oocyte-specific Factor in germline α (Figlα) result in a normal amount of oocytes at birth, but there is a deficiency in establishing the proper connections between the oocyte and surrounding granulosa cells eventually leading to preantral follicle arrest (Soyal et al., (2000)).
The transition between primordial and primary follicles is marked by a squamous to cuboidal transformation of the single layer of granulosa cells surrounding the oocyte. This transformation is impaired in homozygous mutant animals for the winged-helix forkhead transcription factor Foxl2, resulting in a deficiency in granulosa cell differentiation and oocyte atresia (Schmidt (2004)). Upon entrance into the primary stage, oocytes begin to secrete a unique extracellular glycoprotein matrix covering, the zona pellucida. Mutations in zona pellucida components, rather than leading to an early follicular maturation arrest, result in an inability of the ovulated oocyte to adhere to the walls of the oviduct and to be fertilized (Rankin et al., (2000)).
Antral follicle development is characterized by a shift from intraovarian to gonadotropin regulation. In this stage, follicle growth is primarily the result of the formation of a fluid filled compartment, or antrum. Antral follicle development is inhibited in Fshβ homozygous mutant mice, indicating the importance of FSH in this process (Kumar et al., (1997)). Activins and inhibins are two hormones that activate and inhibit FSH, respectively. Mutations in the activin receptor type II (ActRII) gene lead to antral arrest, while females deficient in inhibin, although infertile, can produce fertilizable oocytes after superovulation treatment (Matzuk et al., (1995); Matzuk (1996)). SOD1, a protein that inactivates superoxide radicals, and ZP2 are also necessary for antral development, since mutations in the genes encoding for these two proteins result in a reduction in the number of antral follicles (Matzuk et al., (1998); Rankin (2001)).
The antral follicle will continue to grow until it is ready for ovulation, at which time it is called a Graffian follicle. The process of follicle rupture (ovulation) is induced by a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH), known as luteinization, which resembles the inflammatory response. As the result of this surge, there is an increase in the presence of inflammatory response genes, as well as proteases needed for the rupture of the follicle's basement membrane and the release of the oocyte, highlighting the need for tissue breakdown and repair. Mutations in the inflammatory response genes nitric oxide synthase (Nos), macrophage-stimulating factor 1 receptor (Mstr1), and tumor necrosis factor-induced protein-6 (Tnfip6) result in ovulation deficiencies (Drazen (1999); Fulop (2003); Klein (1998); Waltz (2001)). Female mice mutant for the transcription factor NGFI-A, a direct regulator of the LHβ subunit, are infertile due to a block in ovulation. Administration of LH into these mutant animals restores their fertility, indicating the essential role played by luteinization in normal ovulation (Topilko (1998)). Luteinization is also typified by a termination of granulosa cell proliferation, which is accompanied by a reduction of estrogen production and the induction of progesterone and progesterone receptor (PR) biosynthesis in these cells (Barnett et al., (2006)). Female mice deficient in PR fail to ovulate (Lydon (1995)).
The LH surge induces the oocyte to mature. This event is symbolized by the breakdown of the oocyte nucleus (germinal vesicle breakdown), chromatin condensation, and reinitiation of meiosis. The ovulated oocyte will arrest once again, this time at metaphase II, and will only complete meiosis upon fertilization. Phosphodiesterase 3A (Pde3a) and lunatic fringe (Lfng) are molecules needed for the resumption of oocyte maturation. Mutations in these genes result in infertility because of the inability of the oocytes to proceed past meiosis I (Hahn et al., (2005); Masciarelli (2004)). The G-protein coupled receptor 3 (Gpr3) and c-mos genes are also essential for normal oocyte maturation, but instead of failing to initiate oocyte maturation, mutations in these genes result in the inability of the oocyte to arrest at metaphase II (Ledent (2005)).
6. Müllerian duct formation
The proper formation and differentiation of the Müllerian ducts is an essential developmental process for female reproductive health and the outcome of pregnancy. An early event in the formation of the urogenital system is the cranial-caudal appearance of the Wolffian ducts from the intermediate mesoderm. The formation of the Wolffian duct is followed by a cranial to caudal appearance of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros. While it represents a true excretory organ in fish and amphibians, the pronephros is vestigial in mammals. The mesonephros acts as a fetal kidney only in some mammalian species such as rabbit, pig, sheep, marsupials, and human. The metanephros will develop into the definitive kidney by interacting with the ureteric bud, which sprouts from the caudal region of the Wolffian duct (Bard et al., (1994)). The Müllerian duct or paramesonephric duct arises from an invagination of Lhx1 expressing coelomic epithelium. In the mouse, the Müllerian ducts are formed approximately between E11.75 and E13.5 (Orvis and Behringer (2007)). The Müllerian duct runs parallel to the Wolffian duct, fusing with it distally at the urogenital sinus.
The formation of the Müllerian duct is a two-stage process (see Figure 2). In the first stage, ceolomic mesoepithelial cells at the most anterior part of the mesonephros that are specified to become Müllerian epithelium are seen expressing Lhx1. Wnt4 expression then drives these cells to invaginate and initiate tube formation. In the second stage, the Müllerian duct elongates in between the Wolffian duct and the ceolomic epithelium until it reaches the most caudal tip of the mesonephros, the urogenital sinus, by E13.5 (Orvis and Behringer (2007)). While the first stage of Müllerian duct formation is independent of the presence of the Wolffian duct, the second stage appears to require a fully formed Wolffian duct (Orvis and Behringer (2007)). Mice carrying mutations Lhx1, Pax2, or Emx2 do not develop Müllerian ducts because of the absence of Wolffian ducts (Miyamoto et al., (1997); Kobayashi (2005); Torres et al., (1995)). There are no cellular contributions by the Wolffian duct to the formation of the Müllerian duct despite the fact that the elongating tip of the Müllerian duct is in constant physical contact with the Wolffian duct during its elongation (Orvis and Behringer (2007)). However, mice deficient for the secreted molecule WNT9b, which is expressed in the Wolffian duct epithelium, do not form Müllerian ducts regardless of the presence of Wolffian ducts (Carroll et al., (2005)). This suggests that the Wolffian duct is needed as a physical guide and a source of elongation signals for the Müllerian duct. Retinoic acid signaling is also necessary for Müllerian duct formation. Although, mice mutant for the retinoic acid receptor genes RARa1, RXRa1, RARb2, or RARg have normal female reproductive organs, animals carrying compound mutations in these genes lack Müllerian ducts (Mendelsohn (1994)).
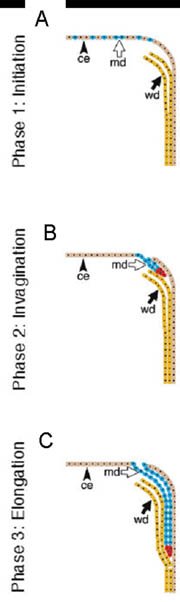
Figure 2. A three phase model for Müllerian duct development. In the first phase, cells of the coelomic epithelium are specified to become Müllerian duct cells A. After specification the second phase begins and these cells invaginate caudally towards the Wolffian duct B. Once the Müllerian duct comes into contact with the Wolffian duct, the third phase begins C and the Müllerian duct elongates caudally, following the path of the Wolffian duct, towards the urogenital sinus. Blue cells; mesoepithelial Müllerian duct cells, red cells; proliferating Müllerian duct precursor cells, brown cells; coelomic epithelial cells, yellow cells; Wolffian epithelial cells. ce; coelomic epithelium, md; Müllerian duct, wd, Wolffian duct.; Orvis and Behringer, Dev Biol 2007, p. 21.
Müllerian duct elongation is also dependent on innate signaling and cellular contributions. Genes such as Wnt4 and Wnt7a, which are expressed in the Müllerian ducts and absent in the Wolffian ducts, are essential for Müllerian duct formation and differentiation. In mice deficient for Wnt4, initial Müllerian duct formation takes place, but it fails to elongate (Vainio et al., (1999)). Wnt7a deficient mice have normal Müllerian duct formation and elongation, but its differentiation into its adult structures, oviduct, uterus and cervix, is compromised (Parr and McMahon (1998)). It has been demonstrated that the proliferation of cells at the elongating tip of the Müllerian duct is an essential cellular process needed for duct elongation (Orvis and Behringer (2007)). Our own observations suggest that in addition to this cell proliferation, cell migration from the most cranial part of the Müllerian duct is also vital for its elongation. We have observed that the PI3K/AKT pathway, which is indispensable for the development of organs composed predominately of tubular structures such as kidney and lung, is also required for Müllerian duct elongation (Fujino (2009)).
7. Müllerian duct regression
Müllerian duct regression normally takes place in males and is mediated MIS (AMH) produced by the embryonic testes (Josso (1993)) (see Figure 3). Mutations in either Mis or its receptors can lead to male pseudohermaphroditism, a condition characterized by retained Müllerian ducts (Behringer et al., (1994); Mishina (1996)). Like many other members of the transforming growth factor ß (TGFß) superfamily, MIS functions by binding to its specific type II receptor (MISR2, a.k.a. AMHR2), which then recruits and phosphorylates a type I receptor to initiate a signaling cascade. Mutations in Wnt7a also lead to male pseudohermaphroditism, perhaps by controlling the expression of Misr2 (Parr and McMahon (1998)). While there is only one type II receptor, evidence has been provided for Alk2 (Acvr1), Alk3 (Bmpr1a) and Alk6 (Bmpr1b) as type I receptors. Bmpr1b has MIS ligand-dependent interaction with MISR2 in Chinese hamster ovary cells (Gouedard (2000)). However, deletion of Bmpr1b led to normal Müllerian duct regression (Clarke (2001)). Conditional inactivation of Bmpr1a resulted in Müllerian duct retention and male pseudohermaphroditism in mice (Jamin et al., (2002)). This is a phenocopy of the Mis and Misr2 knockouts and thus, provides strong evidence for Bmpr1a as the MIS type I receptor in mouse. But, when Bmpr1a conditional mice are bred with transgenic mice overexpressing human MIS, males had regressed Müllerian ducts, suggesting possible redundancy among different type I receptors in the presence of high levels of MIS (Jamin et al., (2003)). Dominant-negative and antisense Acvr1can reverse the function of MIS in P19 embryonic carcinoma cells and in the rat urogenital ridge in organ culture, respectively (Clarke (2001); Visser (2001)). We have shown in rat organ culture that Acvr1is also necessary for the regression of the Müllerian ducts (Zhan (2006)). Furthermore, we have also demonstrated that similar to its formation, Müllerian duct regression is a two-stage process. In the first stage, coelomic epithelial cells expressing Misr2 and the type I receptor Acvr1are induced by MIS to migrate and surround the Müllerian duct while differentiating into mesenchymal cells. Since MIS expression during embryogenesis is male specific, this coelomic epithelial cell migration does not take place in females. In the second stage, the newly transformed mesenchymal cells that now surround the Müllerian ducts, switch their expression of type I receptors from Acvr1 to Bmpr1a. Continuous MIS signaling then triggers a signaling cascade in these mesenchymal cells that culminates in the regression of the Müllerian duct.
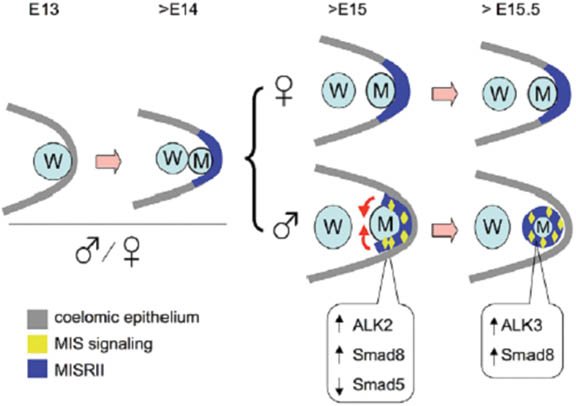
Figure 3. A schematic model of MIS actions at the early stage of Müllerian duct regression. Müllerian duct (M) formation and initial MISRII expression (dark blue) in the coelomic epithelium (gray) are similar in male and female urogenital ridges at E13 and early E14. After ∼E14.5, MIS signaling (yellow) becomes functional in the male, driving the MISRII-expressing cells into the area adjacent to the Müllerian duct and eventually around the Müllerian duct at ∼E15.5. This is an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Meanwhile, MIS also upregulates ALK2 and SMAD8 and downregulates SMAD5. These combined activities have roles in Müllerian duct regression, as noted by the smaller Müllerian duct after E15.5, which disappears eventually. At thistime, ALK3 and SMAD8, which are highly expressed in the Müllerian duct mesenchyme may mediate MIS signaling and Müllerian duct regression. Expression of MISRII remains in the coelomic epithelium of female urogenital ridges during this period. M, Müllerian duct; W, Wolffian duct.; Visser (2001). Reprinted with permission from Zhan et al, Development 2006, p. 2367.
8. Müllerian duct differentiation and uterine maturation
Precise cell fate decisions during differentiation of uterine tissues from the embryonic Müllerian duct are also critical for normal reproductive health and the outcome of pregnancy. Soon after birth, the Müllerian duct differentiates into the adult layers of the uterus: the stromal endometrium or inner mucosal lining, the myometrial muscle layers, and the glandular and luminal epithelium (Kurita et al., (2001)). Despite the relative importance of these tissues for reproduction and thus, continuation of the species, little is known about the molecular mechanisms that regulate their embryonic or postnatal phases of differentiation. Wnt7a, which is expressed in the mesenchyme of the undifferentiated Müllerian duct during embryogenesis and in the luminal epithelia of the postnatal uterus and oviduct, is necessary for controlling postnatal differentiation along the anterior-posterior and radial axes of the epithelial and stromal layers. Mutations in Wnt7a lead to short and uncoiled oviducts, reduced or absent endometrial glands, and a posteriorized female reproductive tract (FRT), where the posterior oviduct becomes similar to the uterus and the uterus obtains characteristics of the vagina (Parr and McMahon (1998)). We have found that conditional deletion of β-catenin in the Müllerian duct mesenchyme before postnatal differentiation of the uterine layers results in a phenotype that is distinct from the phenotype observed by deletion of Wnt7a (Arango (2005)). There are no homeotic transformations, and shortly after birth the uteri of the conditional mutants appear smaller, less organized, and segmented. The uteri of adult conditional β-catenin mutants are grossly deficient in smooth muscle of the myometrium, which has been replaced by adipose. FRT homeotic transformations are more evident in mutants for the homeobox proteins Hoxa10, Hoxa11, and Hoxa13. Mutations in Hoxa10 cause an anterior transformation where the anterior part of the uterus resembles an oviduct (Kobayashi and Behringer (2003)). Similar transformations of the uterus and vagina are seen Hoxa11 and Hoxa13 mutant mice (Kobayashi and Behringer (2003)).
At about 4 weeks after birth, under the regulation of estrogen and the growth factors, epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), and transforming growth factor-α (TGFα), the FRT begins to mature (Couse and Korach (1999)). Estrogen activates the estrogen receptor α (ERα) and ß (ERß), which then bind to estrogen response elements on the promoters of target genes to regulate their expression (Couse and Korach (1999)). In the embryo, ERα is expressed as early as E15.5 in the Müllerian ducts but does not appear to respond to maternal estrogen, while postnatally it is present in the stroma and epithelium of the FRT. ERß expression is low or absent in these tissues. The uterus of mice deficient for ERα (αERKO) is composed of the three adult uterine compartments, myometrium, endometrium, and epithelium, indicting that its initial differentiation from the Müllerian ducts is normal (Couse and Korach (1999); Lubahn (1993)), and not estrogen dependent. However, the total uterine weight is no more than half of its wild-type counterparts. The endometrial stroma is hypoplastic with less organized structure and reduced uterine glands. The typical responses to estrogen induction, i.e. fluid imbibition and the transformation from cuboidal to tall columnar of the luminal epithelial cells, are absent in αERKO, indicating that these animals suffer from estrogen insensitivity. Mice deficient for ERß (ßERKO) do not show a uterine phenotype, which is not surprising in light that ERß is not express in this tissue (Couse and Korach (1999); Krege (1998)).
Estrogen is known to upregulate the levels of EGF, EGFR, IGF1, and TGFα in the uterus (Couse and Korach (1999)). Egf and its receptor Egfr are both expressed in the postnatal uterus (DiAugustine (1988); Huet-Hudson (1990)). Placement of slow-release pellets containing EGF-specific antibody under the kidney capsule of ovariectomized adult female mice 3 days before estrogen treatment, resulted in the inhibition of uterine and vaginal growth (Nelson et al., (1991)). In a complementary experiment, placement of slow-release pellets containing purified EGF under the kidney capsule mimicked the uterine and vaginal response to estrogen (Nelson et al., (1991)). Furthermore, mice carrying a targeted mutation in the Egfr gene exhibited a reduction in the size of the uterus, similar to the one seen for αERKO (Hom (1998)). In the adult uterus, Igf1 transcripts are detected predominantly in the longitudinal myometrium, while the expression of Igf1r is observed throughout the three uterine layers, with higher levels in the lumen and glandular epithelium (Ghahary et al., (1990); Ghahary and Murphy (1989); Murphy and Ghahary (1990)). A targeted mutation of Igf1 resulted in a thin uterus with a total weight of about 13% of that of wild type (Baker (1996)). The myometrium and endometrium were hypoplastic with abnormal uterine glands. Estrogen can also upregulate the expression of TGFα, especially in the uterine epithelium, and an antibody specific for TGFα can block the uterine response to estrogen (Nelson (1992)). The fact that estrogen can regulate the expression levels of Egf, Egfr, Igf1 and Tgfα, combined with the phenotypic similarities in the uterus of mice deficient in these growth factors and ERα, strongly suggests a cross talk between these signaling pathways during uterine maturation.
The presence of an ERα independent uterine response to the estrogenic compound 4-hydroxyestradiol-17ß (4-OH-E2) has been reported (Das (1997)). The potency of 4-OH-E2 to activate an estrogen response in the uterus is similar to that of the primary estrogen 17ß-estradiol (E2); however, its binding affinity to ERα and ERß is 7 to 14-fold less than that of E2 (Das (1997)). Treatment of αERKO and wild type mice with 4-OH-E2 resulted in the characteristic uterine responses to estrogen, fluid imbibition and increase in lactoferrin expression. However, when these animals were treated with E2, only wild type mice exhibited a response. Since ERß is not expressed in the uterus in significant amounts to mediate the observed 4-OH-E2 responses in αERKO, it was concluded that in the uterus there must exist an estrogen receptor-independent response pathway.
Differentiation of the female internal reproductive organs is an essential developmental process not only required for procreation, but also for the well being of the individual. The ovaries are a combination of somatic cells migrating and primordial germ cells, which migrate from the base of the allantois. Defects in migration, differentiation, or function of these cell lineages can result in malformed or absent ovaries, premature ovarian failure, ovarian cysts, ovarian cancers, all of which could compromise reproductive health. Equally important is the development of the uterus from its embryonic anlagen, the Müllerian ducts. Developmental uterine anomalies can result in conditions such as bicornuate uterus, fibroid tumors, endometriosis, uterine leiomyomas, intrauterine adhesions, all of which can lead to pregnancy loss, premature labor, obstructed labor, postpartum hemorrhage, and failure of the embryo to implant, among others. These conditions often require medical intervention, including multiple surgeries.
Copyright: © 2010 Nelson A. Arango and Patricia K. Donahoe
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
§ To whom correspondence should be addressed. E-mail: donahoe.patricia@mgh.harvard.edu
* Edited by Haifan Lin. Last revised July 26, 2010. Published September 30, 2010. This chapter should be cited as: Arango, N.A. and Donahoe, P.K., Sex differentiation in mouse and man and subsequent development of the female reproductive organs (September 30, 2010), StemBook, ed. The Stem Cell Research Community, StemBook, doi/10.3824/stembook.1.53.1, [[UNSUPPORTED:p/uri]] .
References
- Amleh, A. Dean, J. (2002). Mouse genetics provides insight into folliculogenesis, fertilization and early embryonic development. Hum Reprod Update 8(5), 395–403. Abstract DOI
- Anderson, E. Albertini, D.F. (1976). Gap junctions between the oocyte and companion follicle cells in the mammalian ovary. J Cell Biol 71(2), 680–686. Abstract DOI
- Anderson, R. et al. (1999). Mouse primordial germ cells lacking beta1 integrins enter the germline but fail to migrate normally to the gonads. Development 126(8), 1655–1664. Abstract Abstract
- Arango, N.A. et al. (2005). Conditional deletion of beta-catenin in the mesenchyme of the developing mouse uterus results in a switch to adipogenesis in the myometrium. Dev Biol 288(1), 276–283. Abstract DOI
- Baker, J. et al. (1996). Effects of an Igf1 gene null mutation on mouse reproduction. Mol Endocrinol 10(7), 903–918. Abstract DOI
- Bard, J.B. McConnell, J.E. Davies, J.A. (1994). Towards a genetic basis for kidney development. Mech Dev 48(1), 3–11. Abstract DOI
- Bardoni, B. et al. (1994). A dosage sensitive locus at chromosome Xp21 is involved in male to female sex reversal. Nat Genet 7(4), 497–501. Abstract DOI
- Barnett, K.R. Schilling, C. Greenfeld, C.R. Tomic, D. Flaws, J.A. (2006). Ovarian follicle development and transgenic mouse models. Hum Reprod Update 12(5), 537–555. Abstract DOI
- Begum, S. Papaioannou, V.E. Gosden, R.G. (2008). The oocyte population is not renewed in transplanted or irradiated adult ovaries. Hum Reprod 23(10), 2326–2330. Abstract DOI
- Behringer, R.R. Finegold, M.J. Cate, R.L. (1994). Mullerian-inhibiting substance function during mammalian sexual development. Cell 79(3), 415–425. Abstract DOI
- Bel, S. et al. (1998). Genetic interactions and dosage effects of Polycomb group genes in mice. Development 125(18), 3543–3551. Abstract Abstract
- Bristol-Gould, S.K. et al. (2006). Fate of the initial follicle pool: empirical and mathematical evidence supporting its sufficiency for adult fertility. Dev Biol 298(1), 149–154. Abstract DOI
- Buehr, M. Gu, S. McLaren, A. (1993). Mesonephric contribution to testis differentiation in the fetal mouse. Development 117(1), 273–281. Abstract Abstract
- Capel, B. Albrecht, K.H. Washburn, L.L. Eicher, E.M. (1999). Migration of mesonephric cells into the mammalian gonad depends on Sry. Mech Dev 84(1–2), 127–131. Abstract DOI
- Carroll, T.J. Park, J.S. Hayashi, S. Majumdar, A. McMahon, A.P. (2005). Wnt9b plays a central role in the regulation of mesenchymal to epithelial transitions underlying organogenesis of the mammalian urogenital system. Dev Cell 9(2), 283–292. Abstract DOI
- Cattanach, B.M. Iddon, C.A. Charlton, H.M. Chiappa, S.A. Fink, G. (1977). Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone deficiency in a mutant mouse with hypogonadism. Nature 269(5626), 338–340. Abstract DOI
- Clarke, T.R. et al. (2001). Mullerian inhibiting substance signaling uses a bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-like pathway mediated by ALK2 and induces SMAD6 expression. Mol Endocrinol 15(6), 946–959. Abstract DOI
- Colvin, J.S. Green, R.P. Schmahl, J. Capel, B. Ornitz, D.M. (2001). Male-to-female sex reversal in mice lacking fibroblast growth factor 9. Cell 104(6), 875–889. Abstract DOI
- Combelles, C.M. Carabatsos, M.J. Kumar, T.R. Matzuk, M.M. Albertini, D.F. (2004). Hormonal control of somatic cell oocyte interactions during ovarian follicle development. Mol Reprod Dev 69(3), 347–355. Abstract DOI
- Cools, M. Drop, S.L. Wolffenbuttel, K.P. Oosterhuis, J,W. Looijenga, L.H. (2006). Germ cell tumors in the intersex gonad: old paths, new directions, moving frontiers. Endocr Rev 27(5), 468–484. Abstract DOI
- Couse, J.F. Korach, K.S. (1999). Estrogen receptor null mice: what have we learned and where will they lead us?. Endocr Rev 20(3), 358–417.
- Das, S.K. et al. (1997). Estrogenic responses in estrogen receptor-alpha deficient mice reveal a distinct estrogen signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(24), 12786–12791. Abstract DOI
- DiAugustine, R.P. et al. (1988). Influence of estrogens on mouse uterine epidermal growth factor precursor protein and messenger ribonucleic acid. Endocrinology 122(6), 2355–2363. Abstract DOI
- Donovan, P.J. Stott, D. Cairns, L.A. Heasman, J. Wylie, C.C. (1986). Migratory and postmigratory mouse primordial germ cells behave differently in culture. Cell 44(6), 831–838. Abstract DOI
- Drazen, D.L. et al. (1999). Reproductive function in female mice lacking the gene for endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Nitric Oxide 3(5), 366–374. Abstract DOI
- Eggan, K. Jurga, S. Gosden, R. Min, I.M. Wagers, A.J. (2006). Ovulated oocytes in adult mice derive from non-circulating germ cells. Nature 441(7097), 1109–1114. Abstract DOI
- Elvin, J.A. Matzuk, M.M. (1998). Mouse models of ovarian failure. Rev Reprod 3(3), 183–195. Abstract DOI
- Faddy, M. Gosden, R. (2007). Numbers of ovarian follicles and testing germ line renewal in the postnatal ovary: facts and fallacies. Cell Cycle 6(15), 1951–1952. Abstract DOI
- Foster, J.W. et al. (1994). Campomelic dysplasia and autosomal sex reversal caused by mutations in an SRY-related gene. Nature 372(6506), 525–530. Abstract DOI
- Foster, J.W. Graves, J.A. (1994). An SRY-related sequence on the marsupial X chromosome: implications for the evolution of the mammalian testis-determining gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(5), 1927–1931. Abstract DOI
- Fujino, A. et al. (2009). Cell migration and activated PI3K/AKT-directed elongation in the developing rat Mullerian duct. Dev Biol 325(2), 351–362. Abstract DOI
- Fulop, C. et al. (2003). Impaired cumulus mucification and female sterility in tumor necrosis factor-induced protein-6 deficient mice. Development 130(10), 2253–2261. Abstract DOI
- Ghahary, A. Murphy, L.J. (1989). Uterine insulin-like growth factor-I receptors: regulation by estrogen and variation throughout the estrous cycle. Endocrinology 125(2), 597–604. Abstract DOI
- Ghahary, A. Chakrabarti, S. Murphy, L.J. (1990). Localization of the sites of synthesis and action of insulin-like growth factor-I in the rat uterus. Mol Endocrinol 4(2), 191–195. Abstract DOI
- Gobel, U. et al. (2000). Germ-cell tumors in childhood and adolescence. GPOH MAKEI and the MAHO study groups. Ann Oncol 11(3), 263–271. Abstract DOI
- Gouedard, L. et al. (2000). Engagement of bone morphogenetic protein type IB receptor and Smad1 signaling by anti-Mullerian hormone and its type II receptor. J Biol Chem 275(36), 27973–27978. Abstract Abstract
- Greenbaum, M.P. Iwamori, N. Agno, J.E. Matzuk, M.M. (2009). Mouse TEX14 is required for embryonic germ cell intercellular bridges but not female fertility. Biol Reprod 80(3), 449–457. Abstract DOI
- Hahn, K.L. Johnson, J. Beres, B.J. Howard, S. Wilson-Rawls, J. (2005). Lunatic fringe null female mice are infertile due to defects in meiotic maturation. Development 132(4), 817–828. Abstract DOI
- Hom, Y.K. et al. (1998). Uterine and vaginal organ growth requires epidermal growth factor receptor signaling from stroma. Endocrinology 139(3), 913–921. Abstract DOI
- Huang, E.J. et al. (1993). The murine steel panda mutation affects kit ligand expression and growth of early ovarian follicles. Dev Biol 157(1), 100–109. Abstract DOI
- Huet-Hudson, YM. et al. (1990). Estrogen regulates the synthesis of epidermal growth factor in mouse uterine epithelial cells. Mol Endocrinol 4(3), 510–523. Abstract DOI
- Jamin, S.P. Arango, N.A. Mishina, Y. Hanks, M.C. Behringer, R.R. (2002). Requirement of Bmpr1a for Mullerian duct regression during male sexual development. Nat Genet 32(3), 408–410. Abstract DOI
- Jamin, S.P. Arango, N.A. Mishina, Y. Hanks, M.C. Behringer, R.R. (2003). Genetic studies of the AMH/MIS signaling pathway for Mullerian duct regression. Mol Cell Endocrinol 211(1–2), 15–19. Abstract DOI
- Johnson, J. et al. (2005). Oocyte generation in adult mammalian ovaries by putative germ cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood. Cell 122(2), 303–315. Abstract DOI
- Josso, N. et al. (1993). Anti-mullerian hormone: the Jost factor. Recent Prog Horm Res 48, 1–59. Abstract Abstract
- Juneja, S.C. Barr, K.J. Enders, G.C. Kidder, G.M. (1999). Defects in the germ line and gonads of mice lacking connexin43. Biol Reprod 60(5), 1263–1270. Abstract DOI
- Karl, J. Capel, B. (1998). Sertoli cells of the mouse testis originate from the coelomic epithelium. Dev Biol 203(2), 323–333. Abstract DOI
- Katoh-Fukui, Y. et al. (1998). Male-to-female sex reversal in M33 mutant mice. Nature 393(6686), 688–692. Abstract DOI
- Klein, S.L. et al. (1998). Impaired ovulation in mice with targeted deletion of the neuronal isoform of nitric oxide synthase. Mol Med 4(10), 658–664. Abstract Abstract
- Knudson, C.M. Tung, K.S. Tourtellotte, W.G. Brown, G.A. Korsmeyer, S.J. (1995). Bax-deficient mice with lymphoid hyperplasia and male germ cell death. Science 270(5233), 96–99. Abstract DOI
- Kobayashi, A. Behringer, R.R. (2003). Developmental genetics of the female reproductive tract in mammals. Nat Rev Genet 4(12), 969–980. Abstract DOI
- Kobayashi, A. et al. (2005). Distinct and sequential tissue-specific activities of the LIM-class homeobox gene Lim1 for tubular morphogenesis during kidney development. Development 132(12), 2809–2823. Abstract DOI
- Koopman, P. Gubbay, J. Vivian, N. Goodfellow, P. Lovell-Badge, R. (1991). Male development of chromosomally female mice transgenic for Sry. Nature 351(6322), 117–121. Abstract DOI
- Krege, J.H. et al. (1998). Generation and reproductive phenotypes of mice lacking estrogen receptor beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(26), 15677–15682. Abstract DOI
- Kreidberg, J.A. et al. (1993). WT-1 is required for early kidney development. Cell 74(4), 679–691. Abstract DOI
- Kumar, T.R. Wang, Y. Lu, N. Matzuk, M.M. (1997). Follicle stimulating hormone is required for ovarian follicle maturation but not male fertility. Nat Genet 15(2), 201–204. Abstract DOI
- Kurita, T. Cooke, P.S. Cunha, G.R. (2001). Epithelial-stromal tissue interaction in paramesonephric (Mullerian) epithelial differentiation. Dev Biol 240(1), 194–211. Abstract DOI
- Lawson, K.A. et al. (1999). Bmp4 is required for the generation of primordial germ cells in the mouse embryo. Genes Dev 13(4), 424–436. Abstract DOI
- Ledent, C. et al. (2005). Premature ovarian aging in mice deficient for Gpr3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(25), 8922–8926. Abstract DOI
- Lubahn, D.B. et al. (1993). Alteration of reproductive function but not prenatal sexual development after insertional disruption of the mouse estrogen receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90(23), 11162–11166. Abstract DOI
- Luo, X. Ikeda, Y. Parker, K.L. (1994). A cell-specific nuclear receptor is essential for adrenal and gonadal development and sexual differentiation. Cell 77(4), 481–490. Abstract DOI
- Lydon, J.P. et al. (1995). Mice lacking progesterone receptor exhibit pleiotropic reproductive abnormalities. Genes Dev 9(18), 2266–2278. Abstract DOI
- MacLaughlin, D.T. Donahoe, P.K. (2004). Sex determination and differentiation. (Translated from eng). N Engl J Med 350(4), 367–378. (in eng) Abstract DOI
- Mansour, S. Hall, C.M. Pembrey, M.E. Young, I.D. (1995). A clinical and genetic study of campomelic dysplasia. J Med Genet 32(6), 415–420. Abstract DOI
- Martineau, J. Nordqvist, K. Tilmann, C. Lovell-Badge, R. Capel, B. (1997). Male-specific cell migration into the developing gonad. Curr Biol 7(12), 958–968. Abstract DOI
- Masciarelli, S. et al. (2004). Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 3A-deficient mice as a model of female infertility. J Clin Invest 114(2), 196–205. Abstract Abstract
- Matzuk, M.M. Kumar, T.R. Bradley, A. (1995). Different phenotypes for mice deficient in either activins or activin receptor type II. Nature 374(6520), 356–360. Abstract DOI
- Matzuk, M.M. et al. (1996). Transgenic models to study the roles of inhibins and activins in reproduction, oncogenesis, and development. Recent Prog Horm Res 51, 123–154; discussion 155–127. Abstract Abstract
- Matzuk, M.M. Dionne, L. Guo, Q. Kumar, T.R. Lebovitz, R.M. (1998). Ovarian function in superoxide dismutase 1 and 2 knockout mice. Endocrinology 139(9), 4008–4011. Abstract DOI
- McLaren, A. (1991). Development of the mammalian gonad: the fate of the supporting cell lineage. Bioessays 13(4), 151–156. Abstract DOI
- Mendelsohn, C. et al. (1994). Function of the retinoic acid receptors (RARs) during development (II). Multiple abnormalities at various stages of organogenesis in RAR double mutants. Development 120(10), 2749–2771. Abstract Abstract
- Mishina, Y. et al. (1996). Genetic analysis of the Mullerian-inhibiting substance signal transduction pathway in mammalian sexual differentiation. Genes Dev 10(20), 2577–2587. Abstract DOI
- Miyamoto, N. Yoshida, M. Kuratani, S. Matsuo, I. Aizawa, S. (1997). Defects of urogenital development in mice lacking Emx2. Development 124(9), 1653–1664. Abstract Abstract
- Molyneaux, K.A. et al. (2003). The chemokine SDF1/CXCL12 and its receptor CXCR4 regulate mouse germ cell migration and survival. Development 130(18), 4279–4286. Abstract DOI
- Murphy, L.J. Ghahary, A. (1990). Uterine insulin-like growth factor-1: regulation of expression and its role in estrogen-induced uterine proliferation. Endocr Rev 11(3), 443–453. Abstract DOI
- Nef, S. et al. (2003). Testis determination requires insulin receptor family function in mice. Nature 426(6964), 291–295. Abstract DOI
- Nelson, K.G. Takahashi, T. Bossert, N.L. Walmer, D.K. McLachlan, J.A. (1991). Epidermal growth factor replaces estrogen in the stimulation of female genital-tract growth and differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88(1), 21–25. Abstract DOI
- Nelson, K.G. et al. (1992). Transforming growth factor-alpha is a potential mediator of estrogen action in the mouse uterus. Endocrinology 131(4), 1657–1664. Abstract DOI
- Ohinata, Y. et al. (2005). Blimp1 is a critical determinant of the germ cell lineage in mice. Nature 436(7048), 207–213. Abstract DOI
- Orvis, G.D. Behringer, R.R. (2007). Cellular mechanisms of Mullerian duct formation in the mouse. Dev Biol 306(2), 493–504. Abstract DOI
- Parma, P. et al. (2006). R-spondin1 is essential in sex determination, skin differentiation and malignancy. Nat Genet. Abstract Abstract
- Parr, B.A. McMahon, A.P. (1998). Sexually dimorphic development of the mammalian reproductive tract requires Wnt-7a. Nature 395(6703), 707–710. Abstract DOI
- Pepling, M.E. Spradling, A.C. (1998). Female mouse germ cells form synchronously dividing cysts. Development 125(17), 3323–3328. Abstract Abstract
- Pepling, M.E. Spradling, A.C. (2001). Mouse ovarian germ cell cysts undergo programmed breakdown to form primordial follicles. Dev Biol 234(2), 339–351. Abstract DOI
- Perez, G.I. et al. (1999). Prolongation of ovarian lifespan into advanced chronological age by Bax-deficiency. Nat Genet 21(2), 200–203. Abstract DOI
- Rajkovic, A. Pangas, S.A. Ballow, D. Suzumori, N. Matzuk, M.M. (2004). NOBOX deficiency disrupts early folliculogenesis and oocyte-specific gene expression. Science 305(5687), 1157–1159. Abstract DOI
- Rankin, T. Soyal, S. Dean, J. (2000). The mouse zona pellucida: folliculogenesis, fertility and pre-implantation development. Mol Cell Endocrinol 163(1–2), 21–25. Abstract DOI
- Rankin, T.L. et al. (2001). Defective zonae pellucidae in Zp2-null mice disrupt folliculogenesis, fertility and development. Development 128(7), 1119–1126. Abstract Abstract
- Ratts, V.S. Flaws, J.A. Kolp, R. Sorenson, C.M. Tilly, J.L. (1995). Ablation of bcl-2 gene expression decreases the numbers of oocytes and primordial follicles established in the post-natal female mouse gonad. Endocrinology 136(8), 3665–3668. Abstract DOI
- Raverot, G. Weiss, J. Park, S.Y. Hurley, L. Jameson, J.L. (2005). Sox3 expression in undifferentiated spermatogonia is required for the progression of spermatogenesis. Dev Biol 283(1), 215–225. Abstract DOI
- Reddy, J.C. Licht, J.D. (1996). The WT1 Wilms’ tumor suppressor gene: how much do we really know?. Biochim Biophys Acta 1287(1), 1–28. Abstract Abstract
- Russell, L.D. Chiarini-Garcia, H. Korsmeyer, S.J. Knudson, C.M. (2002). Bax-dependent spermatogonia apoptosis is required for testicular development and spermatogenesis. Biol Reprod 66(4), 950–958. Abstract DOI
- Saitou, M. Payer, B. O’Carroll, D. Ohinata, Y. Surani, M.A. (2005). Blimp1 and the emergence of the germ line during development in the mouse. Cell Cycle 4(12), 1736–1740. Abstract Abstract
- Schmidt, D. et al. (2004). The murine winged-helix transcription factor Foxl2 is required for granulosa cell differentiation and ovary maintenance. Development 131(4), 933–942. Abstract DOI
- Schneider, D.T. et al. (2001). Multipoint imprinting analysis indicates a common precursor cell for gonadal and nongonadal pediatric germ cell tumors. Cancer Res 61(19), 7268–7276. Abstract Abstract
- Shawlot, W. Behringer, R.R. (1995). Requirement for Lim1 in head-organizer function. Nature 374(6521), 425–430. Abstract DOI
- Simon, A.M. Goodenough, D.A. Li, E. Paul, D.L. (1997). Female infertility in mice lacking connexin 37. Nature 385(6616), 525–529. Abstract DOI
- Sinclair, A.H. et al. (1990). A gene from the human sex-determining region encodes a protein with homology to a conserved DNA-binding motif. Nature 346(6281), 240–244. Abstract DOI
- Soyal, S.M. Amleh, A. Dean, J. (2000). FIGalpha, a germ cell-specific transcription factor required for ovarian follicle formation. Development 127(21), 4645–4654. Abstract Abstract
- Stallock, J. Molyneaux, K. Schaible, K. Knudson, C.M. Wylie, C. (2003). The pro-apoptotic gene Bax is required for the death of ectopic primordial germ cells during their migration in the mouse embryo. Development 130(26), 6589–6597. Abstract DOI
- Swain, A. Narvaez, V. Burgoyne, P. Camerino, G. Lovell-Badge, R. (1998). Dax1 antagonizes Sry action in mammalian sex determination. Nature 391(6669), 761–767. Abstract DOI
- Swain, A. Lovell-Badge, R. (1999). Mammalian sex determination: a molecular drama. Genes Dev 13(7), 755–767. Abstract DOI
- Taketo, T. Saeed, J. Manganaro, T. Takahashi, M. Donahoe, P.K. (1993). Mullerian inhibiting substance production associated with loss of oocytes and testicular differentiation in the transplanted mouse XX gonadal primordium. Biol Reprod 49(1), 13–23. Abstract DOI
- Tevosian, S.G. et al. (2002). Gonadal differentiation, sex determination and normal Sry expression in mice require direct interaction between transcription partners GATA4 and FOG2. Development 129(19), 4627–4634. Abstract Abstract
- Tilmann, C. Capel, B. (1999). Mesonephric cell migration induces testis cord formation and Sertoli cell differentiation in the mammalian gonad. Development 126(13), 2883–2890. Abstract Abstract
- Topilko, P. et al. (1998). Multiple pituitary and ovarian defects in Krox-24 (NGFI-A, Egr-1)-targeted mice. Mol Endocrinol 12(1), 107–122. Abstract DOI
- Torres, M. Gomez-Pardo, E. Dressler, G.R. Gruss, P. (1995). Pax-2 controls multiple steps of urogenital development. Development 121(12), 4057–4065. Abstract Abstract
- Vainio, S. Heikkila, M. Kispert, A. Chin, N. McMahon, A.P. (1999). Female development in mammals is regulated by Wnt-4 signalling. Nature 397(6718), 405–409. Abstract DOI
- Visser, J.A. et al. (2001). The serine/threonine transmembrane receptor ALK2 mediates Mullerian inhibiting substance signaling. Mol Endocrinol 15(6), 936–945. Abstract DOI
- Visser, J.A. Themmen, A.P. (2005). Anti-Mullerian hormone and folliculogenesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 234(1–2), 81–86. Abstract DOI
- Waltz, S.E. et al. (2001). Ron-mediated cytoplasmic signaling is dispensable for viability but is required to limit inflammatory responses. J Clin Invest 108(4), 567–576. Abstract Abstract
- Yao, H.H. et al. (2004). Follistatin operates downstream of Wnt4 in mammalian ovary organogenesis. Dev Dyn 230(2), 210–215. Abstract DOI
- Ying, Y. Liu, X.M. Marble, A. Lawson, K.A. Zhao, G.Q. (2000). Requirement of Bmp8b for the generation of primordial germ cells in the mouse. Mol Endocrinol 14(7), 1053–1063. Abstract DOI
- Yu, R.N. Ito, M. Saunders, T.L. Camper, S.A. Jameson, J.L. (1998). Role of Ahch in gonadal development and gametogenesis. Nat Genet 20(4), 353–357. Abstract DOI
- Zhan, Y. et al. (2006). Mullerian inhibiting substance regulates its receptor/SMAD signaling and causes mesenchymal transition of the coelomic epithelial cells early in Mullerian duct regression. Development 133(12), 2359–2369. Abstract DOI
- de Sousa Lopes, S.M. et al. (2004). BMP signaling mediated by ALK2 in the visceral endoderm is necessary for the generation of primordial germ cells in the mouse embryo. Genes Dev 18(15), 1838–1849. Abstract DOI